Section 1.3: Lipids
STUDY
Question 1:
While the types of lipids are characterized by structures and functional groups, they all share 2 defining characteristics which are _____ and _____.
→ Low solubility in water
High solubility in non-polar organic solvents
Question 2:
Are lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic, polar or non-polar?
→ Hydrophobic, non-polar
Question 3:
Name 4 major roles of lipids and which type plays which role. Also, briefly explain how lipids have these roles.
→ Energy storage, thermal insulation, and padding
Triacylglycerols
Because lipids have long carbon chains
→ Cellular organization and structure, particularly in membrane
Phospholipids
Because lipids are hydrophobic and assemble into barriers separating aqueous environments
→ Provision of precursor molecules for vitamins and hormones
Some fatty acids (eicosanoids)
Because lipids can pass through cellular membranes, both of which are hydrophobic
→ Regulation of metabolic activities
Steroids
Question 4:
Name 7 major groups of lipids and give an example for each.
→ Fatty acids: omega-3 (found in fish, algae, some plants, and nut oils)
Triacylglycerols: triglyceride
Phospholipids: phosphatidylcholine
Glycolipids: galactocerebroside
Sphingolipids: sphingosine
Steroids: cholesterol
Terpenes: vitamin A1
Question 5:
Fatty acids act as fuel for the body via _____ reaction.
→ Oxidation
Question 6:
Name 3 complex lipids of membrane that have fatty acids as their building blocks.
→ Phospholipids
Glycolipids
Sphingolipids
Question 7:
Fatty acids are composed of _____.
→ Long carbon chains truncated at 1 end by a carboxylic acid
Question 8:
Each fatty acid chain contains an _____ (even or odd) number of carbons.
→ Even
Question 9:
Name 2 subcategories of fatty acids and briefly describe their components.
→ Saturated: only C-C single bonds
Unsaturated: one or more C=C double bonds
Question 10:
High concentration of _____ bonds in fatty acids allows them to store more energy per gram than any other macromolecules in the body.
→ C-H
Question 11:
Most fats reach the cell in the form of _____ which are _____ (components) rather than as _____ which are _____ (components).
→ Free fatty acids
Fatty acid chains not attached to a backbone
Triacylglycerols
3 fatty acid chains attached to a 3-carbon backbone called glycerol
Question 12:
Triacylglycerols, phospholipids, and glycolipids are sometimes referred to as _____.
→ Fatty acids
Question 13:
_____ are the building blocks of phospholipids, glycolipids, and sphingolipids.
→ Fatty acids
Question 14:
Triacylglycerols are also known as _____ or _____.
→ Triglycerides
Fats and oils
Question 15:
Triacylglycerols are composed of a _____-carbon (number) _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains. 3 functions of triacylglycerols are _____.
→ 3
Glycerol
3
Energy storage, thermal insulation, and padding
Question 16:
Adipocytes are specialized fat cells whose cytoplasm contains almost nothing but _____.
→ Triacylglycerols (AKA triglycerides)
Question 17:
Phospholipids are lipids attached to a _____ group.
→ Phosphate
Question 18:
The most important phospholipids are _____.
→ Phosphoglycerides
Question 19:
The simplest phosphoglyceride is _____.
→ Phosphatidic acid
Question 20:
Except phosphatidic acid, all other phosphoglycerides have a phosphatidic acid backbone, which is a _____ backbone attached to a _____ group. This characteristic allows these phosphoglycerides to be referred to ask _____.
→ Glycerol
Phosphate
Phosphatids
Question 21:
Triacylglycerols (AKA _____) are composed of a _____-carbon (number) backbone called _____ attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains, whereas phosphoglycerides are composed of a _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains because _____.
→ Triglycerides
3
Glycerol
3
Glycerol
2
A polar phosphate group replaces 1 of the fatty acid chains
Question 22:
In a phosphoglyceride, the phosphate group lies on the _____ (same or opposite) site of the glycerol from the fatty acids, making the phospholipid _____ (polar or non-polar) at the phosphate end and _____ (polar or non-polar) at the fatty acid end.
→ Opposite
Polar
Non-polar
Question 23:
Molecules that have polar and non-polar ends are referred to as _____.
→ Amphipathic
Question 24:
When forming bilayer membranes, the _____ (polar or non-polar, heads or tails) of phospholipids face toward the watery environment within and outside the cell, while the _____ (polar or non-polar, heads or tails) create an inner layer within the membrane. Generally, the lipid bilayer has _____ (high or low) permeability to polar molecules and _____ (high or low) permeability to non-polar molecules. In other words, the lipid bilayer is _____.
→ Polar heads
Non-polar tails
Low
High
Semi-permeable
Question 25:
Polar molecules are water-_____ (soluble or insoluble) and fat-_____ (soluble or insoluble), whereas non-polar molecules are fat-_____ (soluble or insoluble) and water-_____ (soluble or insoluble).
→ Soluble
Insoluble
Soluble
Insoluble
Question 26:
Phosphoglycerides are composed of a _____-carbon (number) _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains because _____, whereas glycolipids are composed of a _____ backbone attached to one or more _____ instead of to the _____.
→ 3
Glycerol
2
A polar phosphate group replaces 1 of the fatty acid chains
Glycerol
Carbohydrates
Phosphate group
Question 27:
Both phospholipids and glycolipids have polar ends and non-polar ends, making them _____.
→ Amphipathic
Question 28:
Glycolipids are abundant in membranes of _____ cells in human nervous system.
→ Myelinated
Question 29:
Phosphoglycerides are composed of a _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains because _____, whereas sphingolipids are composed of a _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chain.
→ Glycerol
2
A polar phosphate group replaces 1 of the fatty acid chains
Sphingosine
1
Question 30:
In a sphingolipid, the sphingosine backbone molecule is an _____.
→ Amino alcohol
Question 31:
Phospholipids, glycolipids, steroids, and sphingolipids make up part of the cell's _____.
→ Membrane
Question 32:
Steroids are a _____-ringed (number) structure. 4 examples of steroids are _____.
→ 4
Membrane component, hormones, vitamin D, and cholesterol
Question 33:
Terpenes are often part of _____ in the body. 1 example of terpenes is _____ which is important for _____.
→ Pigments
Vitamin A
Vision
Question 34:
Waxes are formed by _____ linkage between a long-chain _____ and a long-chain _____. 1 example of waxes in the human body is _____.
→ Ester
Alcohol
Fatty acid
Ear wax
Question 35:
A characteristic texture of waxes is _____.
→ Water-repellence
Question 36:
A minor group of lipids is eicosanoids, which includes _____, _____, and _____.
→ Prostaglandins
Thromboxanes
Leukotrienes
Question 37:
Eicosanoids are released from cell membranes as local _____ that regulate, among other things, _____, _____, and _____.
→ Hormones
Blood pressure
Body temperature
Smooth muscle contraction
Question 38:
_____ is a commonly used inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis.
→ Aspirin
Question 39:
Because lipids are _____ (soluble or insoluble) in aqueous solution, they're transported in the blood via _____.
→ Insoluble
Lipoproteins
Question 40:
Lipoprotein contains a _____ core surrounded by _____ and _____. Thus, the lipoprotein is able to dissolve lipids in its _____ (hydrophobic or hydrophilic) core and then move freely through the aqueous solution due to its _____ (hydrophobic or hydrophilic) shell.
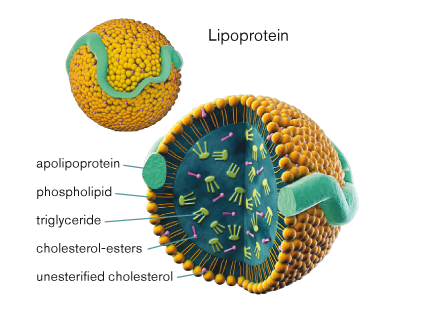
(Source: https://www.mabtech.com/sites/default/files/apolipoprotein-detail_2.png)
→ LipidPhospholipids
Apoproteins
Hydrophobic
Hydrophilic
Question 41:
Lipoproteins are classified by their density. The greater the ratio of lipid to protein, the _____ (lower or higher) the density.
→ Lower
Question 42:
Because proteins weigh more than an equivalent volume of lipids, the greater the ratio of protein to lipid, the _____ (greater or lesser) the density of that lipoprotein.
→ Greater
Question 43:
Name 4 major classes of lipoproteins.
→ Chylomicrons
Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL)
Low density lipoproteins (LDL)
High density lipoproteins (HDL)
Question 44:
Vitamins are a particular type of _____ (organic or inorganic) molecule that are essential. Being essential means that they _____ (can or cannot) be produced by the body. Vitamin _____ (letter) and vitamin _____ (letter) are examples of fat-soluble vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins are transported in the body along with _____ (proteins, carbohydrates, fats, or nucleic acids) obtained from the diet, and also _____ (assist or hinder) the absorption of these macromolecules.
→ Organic
Cannot
A
D
Fats
Assist
PRACTICE
Question 1:
While the types of lipids are characterized by structures and functional groups, they all share 2 defining characteristics which are _____ and _____.
Question 2:
Are lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic, polar or non-polar?
Question 3:
Name 4 major roles of lipids and which type plays which role. Also, briefly explain how lipids have these roles.
Question 4:
Name 7 major groups of lipids and give an example for each.
Question 5:
Fatty acids act as fuel for the body via _____ reaction.
Question 6:
Name 3 complex lipids of membrane that have fatty acids as their building blocks.
Question 7:
Fatty acids are composed of _____.
Question 8:
Each fatty acid chain contains an _____ (even or odd) number of carbons.
Question 9:
Name 2 subcategories of fatty acids and briefly describe their components.
Question 10:
High concentration of _____ bonds in fatty acids allows them to store more energy per gram than any other macromolecules in the body.
Question 11:
Most fats reach the cell in the form of _____ which are _____ (components) rather than as _____ which are _____ (components).
Question 12:
Triacylglycerols, phospholipids, and glycolipids are sometimes referred to as _____.
Question 13:
_____ are the building blocks of phospholipids, glycolipids, and sphingolipids.
Question 14:
Triacylglycerols are also known as _____ or _____.
Question 15:
Triacylglycerols are composed of a _____-carbon _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains. 3 functions of triacylglycerols are _____.
Question 16:
Adipocytes are specialized fat cells whose cytoplasm contains almost nothing but _____.
Question 17:
Phospholipids are lipids attached to a _____ group.
Question 18:
The most important phospholipids are _____.
Question 19:
The simplest phosphoglyceride is _____.
Question 20:
Except phosphatidic acid, all other phosphoglycerides have a phosphatidic acid backbone, which is a _____ backbone attached to a _____ group. This characteristic allows these phosphoglycerides to be referred to ask _____.
Question 21:
Triacylglycerols (AKA _____) are composed of a _____-carbon (number) backbone called _____ attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains, whereas phosphoglycerides are composed of a _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains because _____.
Question 22:
In a phosphoglyceride, the phosphate group lies on the _____ (same or opposite) site of the glycerol from the fatty acids, making the phospholipid _____ (polar or non-polar) at the phosphate end and _____ (polar or non-polar) at the fatty acid end.
Question 23:
Molecules that have polar and non-polar ends are referred to as _____.
Question 24:
When forming bilayer membranes, the _____ (polar or non-polar, heads or tails) of phospholipids face toward the watery environment within and outside the cell, while the _____ (polar or non-polar, heads or tails) create an inner layer within the membrane. Generally, the lipid bilayer has _____ (high or low) permeability to polar molecules and _____ (high or low) permeability to non-polar molecules. In other words, the lipid bilayer is _____.
Question 25:
Polar molecules are water-_____ (soluble or insoluble) and fat-_____ (soluble or insoluble), whereas non-polar molecules are fat-_____ (soluble or insoluble) and water-_____ (soluble or insoluble).
Question 26:
Phosphoglycerides are composed of a _____-carbon (number) _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains because _____, whereas glycolipids are composed of a _____ backbone attached to one or more _____ instead of to the _____.
Question 27:
Both phospholipids and glycolipids have polar ends and non-polar ends, making them _____.
Question 28:
Glycolipids are abundant in membranes of _____ cells in human nervous system.
Question 29:
Phosphoglycerides are composed of a _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chains because _____, whereas sphingolipids are composed of a _____ backbone attached to _____ (number) fatty acid chain.
Question 30:
In a sphingolipid, the sphingosine backbone molecule is an _____.
Question 31:
Phospholipids, glycolipids, steroids, and sphingolipids make up part of the cell's _____.
Question 32:
Steroids are a _____-ringed (number) structure. 4 examples of steroids are _____.
Question 33:
Terpenes are often part of _____ in the body. 1 example of terpenes is _____ which is important for _____.
Question 34:
Waxes are formed by _____ linkage between a long-chain _____ and a long-chain _____. 1 example of waxes in the human body is _____.
Question 35:
A characteristic texture of waxes is _____.
Question 36:
A minor group of lipids is eicosanoids, which includes _____, _____, and _____.
Question 37:
Eicosanoids are released from cell membranes as local _____ that regulate, among other things, _____, _____, and _____.
Question 38:
_____ is a commonly used inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis.
Question 39:
Because lipids are _____ (soluble or insoluble) in aqueous solution, they're transported in the blood via _____.
Question 40:
Lipoprotein contains a _____ core surrounded by _____ and _____. Thus, the lipoprotein is able to dissolve lipids in its _____ (hydrophobic or hydrophilic) core and then move freely through the aqueous solution due to its _____ (hydrophobic or hydrophilic) shell.

(Source: https://www.mabtech.com/sites/default/files/apolipoprotein-detail_2.png)
Question 41:
Lipoproteins are classified by their density. The greater the ratio of lipid to protein, the _____ (lower or higher) the density.
Question 42:
Because proteins weigh more than an equivalent volume of lipids, the greater the ratio of protein to lipid, the _____ (greater or lesser) the density of that lipoprotein.
Question 43:
Name 4 major classes of lipoproteins.
Question 44:
Vitamins are a particular type of _____ (organic or inorganic) molecule that are essential. Being essential means that they _____ (can or cannot) be produced by the body. Vitamin _____ (letter) and vitamin _____ (letter) are examples of fat-soluble vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins are transported in the body along with _____ (proteins, carbohydrates, fats, or nucleic acids) obtained from the diet, and also _____ (assist or hinder) the absorption of these macromolecules.
ANSWER KEY
Question 1:
→ Low solubility in water
High solubility in non-polar organic solvents
Question 2:
→ Hydrophobic, non-polar
Question 3:
→ Energy storage, thermal insulation, and padding
Triacylglycerols
Because lipids have long carbon chains
→ Cellular organization and structure, particularly in membrane
Phospholipids
Because lipids are hydrophobic and assemble into barriers separating aqueous environments
→ Provision of precursor molecules for vitamins and hormones
Some fatty acids (eicosanoids)
Because lipids can pass through cellular membranes, both of which are hydrophobic
→ Regulation of metabolic activities
Steroids
Question 4:
→ Fatty acids: omega-3 (found in fish, algae, some plants, and nut oils)
Triacylglycerols: triglyceride
Phospholipids: phosphatidylcholine
Glycolipids: galactocerebroside
Sphingolipids: sphingosine
Steroids: cholesterol
Terpenes: vitamin A1
Question 5:
→ Oxidation
Question 6:
→ Phospholipids
Glycolipids
Sphingolipids
Question 7:
→ Long carbon chains truncated at 1 end by a carboxylic acid
Question 8:
→ Even
Question 9:
→ Saturated: only C-C single bonds
Unsaturated: one or more C=C double bonds
Question 10:
→ C-H
Question 11:
→ Free fatty acids
Fatty acid chains not attached to a backbone
Triacylglycerols
3 fatty acid chains attached to a 3-carbon backbone called glycerol
Question 12:
→ Fatty acids
Question 13:
→ Fatty acids
Question 14:
→ Triglycerides
Fats and oils
Question 15:
→ 3
Glycerol
3
Energy storage, thermal insulation, and padding
Question 16:
→ Triacylglycerols (AKA triglycerides)
Question 17:
→ Phosphate
Question 18:
→ Phosphoglycerides
Question 19:
→ Phosphatidic acid
Question 20:
→ Glycerol
Phosphate
Phosphatids
Question 21:
→ Triglycerides
3
Glycerol
3
Glycerol
2
A polar phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains
Question 22:
→ Opposite
Polar
Non-polar
Question 23:
→ Amphipathic
Question 24:
→ Polar heads
Non-polar tails
Low
High
Semi-permeable
Question 25:
→ Soluble
Insoluble
Soluble
Insoluble
Question 26:
→ 3
Glycerol
2
A polar phosphate group replaces 1 of the fatty acid chains
Glycerol
Carbohydrates
Phosphate group
Question 27:
→ Amphipathic
Question 28:
→ Myelinated
Question 29:
→ Glycerol
2
A polar phosphate group replaces 1 of the fatty acid chains
Sphingosine
1
Question 30:
→ Amino alcohol
Question 31:
→ Membrane
Question 32:
→ 4
Membrane component, hormones, vitamin D, and cholesterol
Question 33:
→ Pigments
Vitamin A
Vision
Question 34:
→ Ester
Alcohol
Fatty acid
Ear wax
Question 35:
→ Water-repellence
Question 36:
→ Prostaglandins
Thromboxanes
Leukotrienes
Question 37:
→ Hormones
Blood pressure
Body temperature
Smooth muscle contraction
Question 38:
→ Aspirin
Question 39:
→ Insoluble
Lipoproteins
Question 40:
→ Lipid
Phospholipids
Apoproteins
Hydrophobic
Hydrophilic
Question 41:
→ Lower
Question 42:
→ Greater
Question 43:
→ Chylomicrons
Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL)
Low density lipoproteins (LDL)
High density lipoproteins (HDL)
Question 44:
→ Organic
Cannot
A
D
Fats
Assist
No comments:
Post a Comment