Section 1.5: Nucleotides
STUDY
Question 1:
Nucleotides involve in the cell's use of _____ and comprising the building blocks of every organism's _____. They're composed of 3 components: _____, _____, and _____.
→ Energy
Genetic material
A 5-carbon (pentose) sugar
A nitrogenous base
A phosphate group
**Review**
(Source: http://image.slidesharecdn.com/organicchemistry-131105135539-phpapp02/95/organic-chemistry-7-638.jpg?cb=1383659789)
Question 2:
In DNA, the highly stable _____, along with the _____, are able to link together to form a stable and organized backbone.
→ Sugars
Phosphate groups
Question 3:
Both sugars and phosphate groups are _____ (polar or non-polar) and, thus, can face _____ (outward or inward) into the watery solvent of the cell.
→ Polar
Outward
Question 4:
Nitrogenous bases can form _____ (weak, moderate, or strong) _____ bonds with each other that stabilize the _____-stranded (single or double) structure of DNA but can also be separated to allow the replication of genetic material.
→ Weak
Hydrogen
Double
Question 5:
Nucleoside = _____ sugar + _____ base + _____ (number) phosphate groups
Nucleotide = _____ sugar + _____ base + _____ (number) phosphate groups
→ Pentose
Nitrogenous
0
Pentose
Nitrogenous
1 or more
Question 6:
Nucleotides are _____ (monomers or polymers), whereas nucleic acids are _____ (monomers or polymers). _____ (nucleotides or nucleic acids) form polymers to create _____ (nucleotides or nucleic acids).
→ Monomers
Polymers
Nucleotides
Nucleic acids
Question 7:
Nucleotides form polymers to create nucleic acids, _____ and _____, which allow for expression of genetic traits by specifying the production of _____ (carbohydrates, proteins, or lipids).
→ DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid)
RNA (RiboNucleic Acid)
Proteins
Question 8:
In nucleic acids, nucleotides are joined together into long strands by _____ bonds between phosphate group of 1 nucleotide and 3rd carbon of pentose sugar of the other nucleotide, forming a _____ backbone.
→ Phosphodiester
Sugar-phosphate
Question 9:
Nucleotides are written in the _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') direction, so that the top strand runs _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') and the bottom strand runs _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5').
→ 5' to 3'
5' to 3'
3' to 5'
Question 10:
Name 4 nitrogenous bases and their abbreviation in DNA. Identify which 2 are purines and which 2 are pyrimidines. Identify complementary strands and how many H-bonds are formed between them, with " = " means 2 H-bonds and " ≡ " means 3 H-bonds.
→ Adenine (A) = Thymine (T)
Guanine (G) ≡ Cytosine (C)
**Mnemonic**
Pyrimidine: cytosine and thymine
Question 11:
Purine is a _____-ringed (number) structure, whereas pyrimidine is a _____-ringed (number) structure.
→ 2
1
Question 12:
DNA usually exists in double-stranded structure described by the _____ model, named after 2 scientists who are credited with 1st theorizing DNA structure.
→ Watson-Crick
**Self-notes**
Special thanks to Rosalind Franklin, an unsung hero
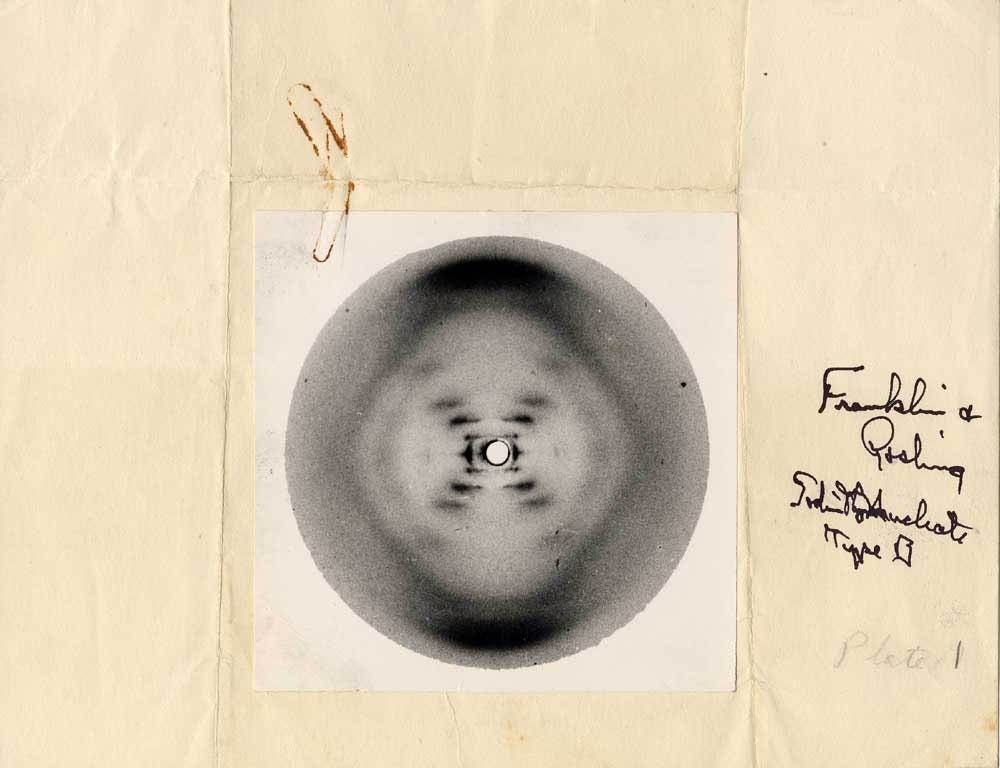
(Source: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/sites/default/files/resources/articles/crystal_clear/Rosalind_Franklin_Plate_1_DNA_B_form_1000.jpg)
In double-stranded structure, AKA the B form, the 2 strands run side-by-side in opposite _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') direction (thus, anti-parallel) bound together by _____ bonds between nitrogenous bases. This bonding is often referred to as _____. The length of DNA strands is measured in _____.
→ 3' to 5'
Hydrogen
Base-pairing
Base-pair (bp)
Question 14:
2 strands that match up in the correct order with each other are called _____ strands. When they bind together, they curl into a _____ which contains 2 distinct grooves called the _____ and the _____. Each groove spirals _____ (once or twice) around the structure for every _____ (number) base-pairs. This DNA structure is _____ (stable or unstable) in the cellular environment and allows for replication of genetic material.
→ Complementary
Double helix
Major groove
Minor groove
Once
10
Stable
(Source: http://www.biologynoteshelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/MAJOR-AND-MINOR-GROOVES-210x300.jpg)
(Source: https://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/251/flashcards/704251/png/grooves1316409303998.png)
Question 15:
DNA (which stands for _____) is a polymer of _____, each of which is composed of 3 parts: _____, _____, and _____. Purines are _____ and _____, whereas pyrimidines are _____ and _____.
→ DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
Nucleotides
Phosphate group
5-carbon (pentose) sugar
Question 16:
_____, a nitrogenous base in RNA that is complementary to Adenine, is a _____ (purine or pyrimidine).
→ Uracil
Pyrimidine
Question 17:
2 _____ (phosphodiester bonds or H-bonds) hold Adenine and Thymine together, whereas 3 _____ (phosphodiester bonds or H-bonds) hold Guanine and Cytosine together. This means that more energy is required to separate _____ (Adenine = Thymine bond or Guanine ≡ Cytosine bond).
→ H-bonds
H-bonds
Guanine ≡ Cytosine bond
Question 18:
RNA (which stands for _____) is identical to DNA (which stands for _____) in structure except that:
1. Carbon #_____ on pentose sugar is not _____, meaning that it has a _____ group attached;
2. RNA is almost always _____-stranded (single or double); and
3. RNA contains the pyrimidine _____ instead of _____, both of which are complementary to _____.
→ RiboNucleic Acid
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
2
Deoxygenated
Hydroxyl
Single
Uracil (U)
Thymine (T)
Adenine (A)
Question 19:
Unlike DNA, RNA _____ (can or cannot) move through the nuclear pores and _____ (is or is not) confined to the nucleus.
→ Can
Is not
Question 20:
3 important types of RNA are _____ (which stands for _____), _____ (which stands for _____), and _____ (which stands for _____).
→ mRNA
Messenger RNA
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA
tRNA
Transfer RNA
Question 21:
A common cause of mutations in DNA is the similarity in structure between uracil and thymine. Draw their structures and circle what differentiates one from the other.
→

(Source: https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj6od2aRe-5rGq2YDGsfjX642n1x_hdfABgk2nDtl07__kVwKU-TM5wkRiBUCAV2lUEqEKWrmte38eeKQYo3Woley4fFeqtkddfd4BR-Fr7bAchEmbtgVImVZZKF9PGhouWQLueQG-4Xp8b/s1600/uracil-thymine.png)
Question 22:
Draw the structures of Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. Demonstrate which ones pair together and how they pair.
→

(Source: https://biochemistry3rst.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/hydrogen-bonds.gif)
Question 23:
In addition to forming genetic material, nucleotides also serve other purposes in the cell. Name 4 other important nucleotides and briefly describe their purposes.
→ ATP (= Adenosine TriPhosphate): main source of readily available energy for the cell
cAMP (= cyclic AMP): important component in many second messenger systems
NADH and FADH2: co-enzymes involved in Krebs cycle
PRACTICE
Question 1:
Nucleotides involve in the cell's use of _____ and comprising the building blocks of every organism's _____. They're composed of 3 components: _____, _____, and _____.
Question 2:
In DNA, the highly stable _____, along with the _____, are able to link together to form a stable and organized backbone.
Question 3:
Both sugars and phosphate groups are _____ (polar or non-polar) and, thus, can face _____ (outward or inward) into the watery solvent of the cell.
Question 4:
Nitrogenous bases can form _____ (weak, moderate, or strong) _____ bonds with each other that stabilize the _____-stranded (single or double) structure of DNA but can also be separated to allow the replication of genetic material.
Question 5:
Nucleoside = _____ sugar + _____ base + _____ (number) phosphate groups
Nucleotide = _____ sugar + _____ base + _____ (number) phosphate groups
Question 6:
Nucleotides are _____ (monomers or polymers), whereas nucleic acids are _____ (monomers or polymers). _____ (nucleotides or nucleic acids) form polymers to create _____ (nucleotides or nucleic acids).
Question 7:
Nucleotides form polymers to create nucleic acids, _____ and _____, which allow for expression of genetic traits by specifying the production of _____ (carbohydrates, proteins, or lipids).
Question 8:
In nucleic acids, nucleotides are joined together into long strands by _____ bonds between phosphate group of 1 nucleotide and 3rd carbon of pentose sugar of the other nucleotide, forming a _____ backbone.
Question 9:
Nucleotides are written in the _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') direction, so that the top strand runs _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') and the bottom strand runs _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5').
Question 10:
Name 4 nitrogenous bases and their abbreviation in DNA. Identify which 2 are purines and which 2 are pyrimidines. Identify complementary strands and how many H-bonds are formed between them, with " = " means 2 H-bonds and " ≡ " means 3 H-bonds.
Question 11:
Purine is a _____-ringed (number) structure, whereas pyrimidine is a _____-ringed (number) structure.
Question 12:
DNA usually exists in double-stranded structure described by the _____ model, named after 2 scientists who are credited with 1st theorizing DNA structure.
In double-stranded structure, AKA the B form, the 2 strands run side-by-side in opposite _____ (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') direction (thus, anti-parallel) bound together by _____ bonds between nitrogenous bases. This bonding is often referred to as _____. The length of DNA strands is measured in _____.
Question 14:
2 strands that match up in the correct order with each other are called _____ strands. When they bind together, they curl into a _____ which contains 2 distinct grooves called the _____ and the _____. Each groove spirals _____ (once or twice) around the structure for every _____ (number) base-pairs. This DNA structure is _____ (stable or unstable) in the cellular environment and allows for replication of genetic material.
Question 15:
DNA (which stands for _____) is a polymer of _____, each of which is composed of 3 parts: _____, _____, and _____. Purines are _____ and _____, whereas pyrimidines are _____ and _____.
Question 16:
_____, a nitrogenous base in RNA that is complementary to Adenine, is a _____ (purine or pyrimidine).
Question 17:
2 _____ (phosphodiester bonds or H-bonds) hold Adenine and Thymine together, whereas 3 _____ (phosphodiester bonds or H-bonds) hold Guanine and Cytosine together. This means that more energy is required to separate _____ (Adenine = Thymine bond or Guanine ≡ Cytosine bond).
Question 18:
RNA (which stands for _____) is identical to DNA (which stands for _____) in structure except that:
1. Carbon number _____ on pentose sugar is not _____, meaning that it has a _____ group attached;
2. RNA is almost always _____-stranded (single or double); and
3. RNA contains the pyrimidine _____ instead of _____, both of which are complementary to _____.
Question 19:
Unlike DNA, RNA _____ (can or cannot) move through the nuclear pores and _____ (is or is not) confined to the nucleus.
Question 20:
3 important types of RNA are _____ (which stands for _____), _____ (which stands for _____), and _____ (which stands for _____).
Question 21:
A common cause of mutations in DNA is the similarity in structure between uracil and thymine. Draw their structures and circle what differentiates one from the other.
Question 22:
Draw the structures of Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. Demonstrate which ones pair together and how they pair.
Question 23:
In addition to forming genetic material, nucleotides also serve other purposes in the cell. Name 4 other important nucleotides and briefly describe their purposes.
ANSWER KEY
Question 1:
→ Energy
Genetic material
A 5-carbon (pentose) sugar
A nitrogenous base
A phosphate group
**Review**
(Source: http://image.slidesharecdn.com/organicchemistry-131105135539-phpapp02/95/organic-chemistry-7-638.jpg?cb=1383659789)
Question 2:
→ Sugars
Phosphate groups
Question 3:
→ Polar
Outward
Question 4:
→ Weak
Hydrogen
Double
Question 5:
→ Pentose
Nitrogenous
0
Pentose
Nitrogenous
1 or more
Question 6:
→ Monomers
Polymers
Nucleotides
Nucleic acids
Question 7:
→ DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid)
RNA (RiboNucleic Acid)
Proteins
Question 8:
→ Phosphodiester
Sugar-phosphate
Question 9:
→ 5' to 3'
5' to 3'
3' to 5'
Question 10:
→ Adenine (A) = Thymine (T)
Guanine (G) ≡ Cytosine (C)
**Mnemonic**
Pyrimidine: cytosine and thymine
Question 11:
→ 2
1
Question 12:
→ Watson-Crick
→ 3' to 5'
Hydrogen
Base-pairing
Base-pair (bp)
Question 14:
→ Complementary
Double helix
Major groove
Minor groove
Once
10
Stable
(Source: http://www.biologynoteshelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/MAJOR-AND-MINOR-GROOVES-210x300.jpg)
(Source: https://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/251/flashcards/704251/png/grooves1316409303998.png)
Question 15:
→ DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
Nucleotides
Phosphate group
5-carbon (pentose) sugar
Question 16:
→ Uracil
Pyrimidine
Question 17:
→ H-bonds
H-bonds
Guanine ≡ Cytosine bond
Question 18:
→ RiboNucleic Acid
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
2
Deoxygenated
Hydroxyl
Single
Uracil (U)
Thymine (T)
Adenine (A)
Question 19:
→ Can
Is not
Question 20:
→ mRNA
Messenger RNA
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA
tRNA
Transfer RNA
Question 21:
→

(Source: https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj6od2aRe-5rGq2YDGsfjX642n1x_hdfABgk2nDtl07__kVwKU-TM5wkRiBUCAV2lUEqEKWrmte38eeKQYo3Woley4fFeqtkddfd4BR-Fr7bAchEmbtgVImVZZKF9PGhouWQLueQG-4Xp8b/s1600/uracil-thymine.png)
Question 22:
→

(Source: https://biochemistry3rst.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/hydrogen-bonds.gif)
Question 23:
→ ATP (= Adenosine TriPhosphate): main source of readily available energy for the cell
cAMP (= cyclic AMP): important component in many second messenger systems
NADH and FADH2: co-enzymes involved in Krebs cycle



Even I have been preparing for LSAT and it is hard to wake up in the morning and then travel to the classes. I feel exhausted so now will quit the coaching class and would be signing up with Online LSAT Prep course to eliminate the travel time. I can utilize that time for meditation, yoga and some other activity that will benefit me with the study.
ReplyDeleteI have being on blog Sites for a while now and today I felt like I should share my story because I was a victim too. I had HIV for 6 years and i never thought I would ever get a cure I had and this made it impossible for me to get married to the man I was supposed to get married to even after 2 years of relationship he broke up with me when he finds out I was HIV positive. So I got to know about Dr. Itua on Blog Site who treated someone and the person shared a story of how she got a cured and let her contact details, I contacted Dr. Itua and he actually confirmed it and I decided to give a try too and use his herbal medicine that was how my burden ended completely. My son will be 2 soon and I am grateful to God and thankful to his medicine too.Dr Itua Can As Well Cure The Following Disease… Cancer, HIV, Herpes, Hepatitis B, Liver Inflammatory,Diabetes,Fibroid, Get Your Ex Back, If you have (A just reach him on drituaherbalcenter@gmail.com Or Whatsapp Number.+2348149277967)He can also advise you on how to handle some marital's issues. He's a good man.
ReplyDeleteAs a global Contract Research Organization (CRO), headquartered in New York, USA, Alfa Chemistry has served the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries for eight years. Pyrimidines
ReplyDelete